Miscarriage is the loss of a pregnancy earlier than twenty weeks gestation. There are many issues for early miscarriage or pregnancy loss. In many cases, no reason for miscarriage is identified. Most conditions of miscarriage are not preventable. It is important to remember that ladies who have a miscarriage(s) still have a good chance for a successful pregnancy in future.
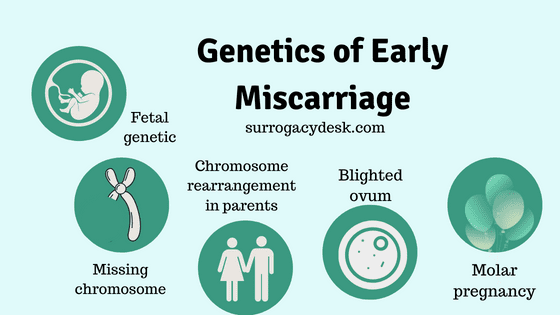
Genetic causes of early miscarriage
Fetal chromosomal abnormalities
Approximately 50% of first trimester miscarriages are because of a chromosome abnormality in the fetus. Chromosomes are the inherited structures in the cells of bodies. A child has copies of each chromosome — one inherited from the mother in the egg, and the alternative inherited from the father in the sperm. Each chromosome holds hundreds to thousands of genes that are responsible for growth and development. A more chromosome or a lacking chromosome can reason miscarriage, typically in the first or second trimester of being pregnant. It can result in an infant with mental abilities or intellectual disability and defects. Once a pair has had a being pregnant affected by a chromosome abnormality, there’s a slightly extra risk for his or her future pregnancies to be affected with chromosome abnormalities. In a few cases prenatal diagnosis, such as chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis, are suggested in future pregnancies.
Inherited chromosomal Rearrangement
An inherited variation with the chromosomes also can be the reason for miscarriage. A fetus can have a rearrangement of his or her chromosomes, wherein the chromosomes are dependent differently. The baby doesn’t have health problems because, even though his or her chromosomes are rearranged, these are balanced. Consequently, there are no missing of the chromosomes. However, due to the manner the chromosomes are passed from parents to child, the infant may also inherit more or missing pieces of a chromosome. Extra and lacking genetic material lead to “chromosomal imbalance” and might reduce intellectual capacity. In such case, it results in defects in a live born or reason a miscarriage. For couples who have had a couple of miscarriages, the threat that one of the mother and father has a chromosomal rearrangement is approximately 3-6%. While mother and father who deliver chromosomal rearrangements are at increased chance to have further miscarriages or infants born with health issues, they also can produce healthy children. Chromosome research may be performed on mother and father’ blood to see if both parent is a provider of a chromosomal rearrangement.

Gene mutation
Another genetic reason of miscarriage is a change (mutation) in a single or more genes on the chromosomes. This can reason specific genetic diseases or delivery defects. Mutations can occur spontaneously in pregnancies or may be inherited from mother and father who themselves are healthy. Birth defects related to those situations can sometimes be detected throughout being pregnant by a sonogram. If there’s a record of a selected disease in a parent or family member, single gene disorders may be tested for prenatally in a few cases.
Problems with the gene or chromosome
Most miscarriages occur due to the fact the fetus isn’t always growing as expected. About 50 % of miscarriages are related to more or missing chromosomes. Most often, chromosome issues end result from errors that occur through chance because the embryo divides and grows
Blighted Ovum
A blighted ovum is commonly as a result of chromosomal or genetic issues at some point of cell division. During conception, the egg will begin to divide rapidly after being fertilized through sperm. Around 10 days later, the cells have formed an embryo. With a blighted ovum, the embryo never forms or stops developing after it are formed.
Molar pregnancy and partial molar pregnancy
Molar pregnancy, each sets of chromosomes come from the father. A molar being pregnant is related to ordinary growth of the placenta; there’s typically no fetal development. A partial molar being pregnant happens when the mother’s chromosomes remain, however the father gives sets of chromosomes. A partial molar pregnancy is typically related to abnormalities of the placenta, and an abnormal fetus. Molar and partial molar pregnancies aren’t viable pregnancies. Molar and partial molar pregnancies can sometimes be related to cancerous modifications of the placenta.
Invasive prenatal tests
Some invasive prenatal genetic tests, together with chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis, carry a moderate chance of miscarriage.
Intrauterine fetal demise
In this situation, an embryo forms but stops developing and dies earlier than any signs and symptoms of being pregnant loss occur.
Previous miscarriages
Women who’ve had or more consecutive miscarriages are at higher chance of miscarriage
Uterine or cervical problems
Certain uterine situations or weak cervical tissues (incompetent cervix) would possibly increase the chance of miscarriage.
Smoking, alcohol and illicit drugs
Women who smoke at some point of being pregnant have a more chance of miscarriage than do nonsmokers. Heavy alcohol use and illicit drug use additionally increase the chance of miscarriage
Maternal Health Issues
Other reasons for being pregnant loss are associated with maternal health. An abnormally formed uterus can cause being pregnant loss. Health problems consisting of hormonal imbalance, poorly-controlled diabetes, and different immune system abnormalities, kidney and heart disease, and high blood pressure can create problems in carrying a being pregnant to term. These reasons of miscarriage may be evaluated through blood assessments and a sonogram of the uterus
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Infections
- Hormonal problems
- Uterus or cervix problems
- Thyroid disease
What does NOT cause miscarriage
Routine activities consisting of those do not initiate a miscarriage:
- Exercise, such as high-depth activities consisting of jogging and cycling.
- Sexual intercourse.
- Working environment not exposed to dangerous chemical substances or radiation. Talk together along with your doctor in case is involved about work-associated risks.
Take a regular multivitamin. Limit your coffee intake. Consuming extra than caffeinated liquids an afternoon regarded to be related to a higher chance of miscarriage.
Read More